Create the Red Hat OpenShift cluster
1 .Login to load balancer VM
Create the directories that will be used by the OpenShift Container Platform installation process
mkdir /var/www/html/ocp
mkdir /var/www/html/ignitions
mkdir /root/ocp-install
3 .Download the required files
cd /root/ocp-install
curl -o openshift-install.tar.gz 'https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/s390x/clients/ocp/4.13.4/openshift-install-linux-4.13.4.tar.gz'
curl -o openshift-client-linux.tar.gz 'https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/s390x/clients/ocp/4.13.4/openshift-client-linux-4.13.4.tar.gz'
4 .Download the rootfs file that is used for the creation of the Red Hat OpenShift cluster nodes.
cd /var/www/html/ocp
curl -o rhcos-installer-rootfs.s390x.img 'https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/s390x/dependencies/rhcos/4.13/4.13.0/rhcos-installer-rootfs.s390x.img'
5 .Create a symbolic link to the file
ln -s rhcos-installer-rootfs.s390x.img rootfs.img
6 .Untar and unzip the downloaded files
The openshift-client-linux.tar.gz file contains the client tools that will be used to interact with your cluster.
cd /root/ocp-install
tar zxvf openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
README.md
oc
kubectl
7 .Move the files that are extracted from the previous step to the /usr/local/bin to have access to these tools from your user path
mv oc /usr/local/bin
mv kubectl /usr/local/bin
8 .Prepare the openshift-install binary for the next steps of the Red Hat OpenShift installation.
cd /root/ocp-install
tar zxvf openshift-install.tar.gz
README.md
openshift-install
chmod +x openshift-install
9 .Create a directory to keep ocp-generated installation files
mkdir /root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy
10 .Copy the installation configuration file for Red Hat OpenShift
copy install-config.yamlto /root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy directory
11 Add pull secret and SSH key
Edit two sections of the install-config.yaml file. The following image illustrates those steps, showing how to find the SSH key and the pull secret and where to add them.
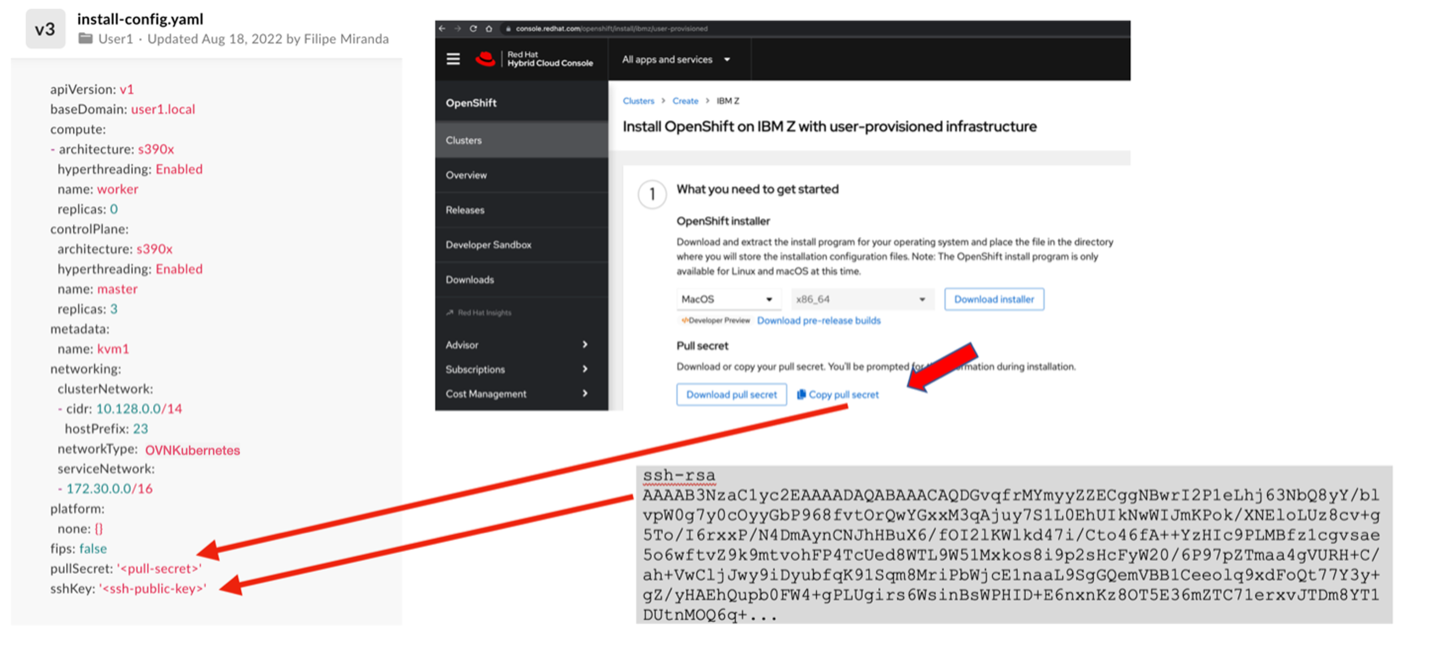
11.1 Generate the SSH key
Generate the SSH key in load balancer VM, which will be used to access nodes when Red Hat OpenShift is deployed
Generate the SSH key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
copy the ssh-public-key
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Ensure that in the install-config.yaml file, “ssh-public-key” variables is updated with the copied value enclosed in single quotation mark
11.2 Get pull secret
To access the pull secret, you must have a Red Hat account with a valid Red Hat OpenShift subscription
We can also create a new account and use trial Liscence which will expire in 60 days
In install-config.yaml file, replace the values of the “pull-secret” with the correct values from the account https://console.redhat.com/openshift/install/pull-secret
12 Create Kubernetes manifest files
# create kubernetes manifests
./openshift-install create manifests --dir=/root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy
To set masters are not schedulable :
-
Open the manifests/cluster-scheduler-02-config.ymlfile
-
Locate the mastersSchedulable parameter and set its value to false
-
Save and exit the file
13 Create ignition config files
# create ignition config files
./openshift-install create ignition-configs --dir=/root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy
Copy the files master.ign, worker.ign, and bootstrap.ign to /var/www/html/ignitions/ in load balancer node where we have configured an HTTP server (Apache) to serve these files during the creation of the RHCOS VMs
cp /root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy/bootstrap.ign /root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy/master.ign /root/ocp-install/ocp-deploy/worker.ign /var/www/html/ignitions/
chmod o+xr /var/www/html/ignitions/*.ign